4.1 Introduction
Learning Objectives
- Identify and use the symbols found in Pedigree Charts.
- Analyze Pedigree Charts to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of individuals in the chart.
- Identify the pattern of inheritance of autosomal dominant and recessive traits in humans.
- Relate the chromosome theory of inheritance to Mendelian principles.
In Chapter 1, we discussed “model genetic organisms” — these are organisms with characteristics that make them useful for genetic analysis. Such as, short generation time, production of numerous progeny, and the ability to be reared in a laboratory environment. Humans are not model genetic organisms; there are no pre-breeding lines, controlled matings are not possible, generation time is relatively long, and progeny numbers are too small to conduct statistical analyses on. Some techniques, such as test crosses, can only be performed with model organisms or other species that can be experimentally manipulated. As such, we are unable to perform controlled crosses with humans, and therefore, in order to be able to study the pattern of inheritance of traits in humans, we look at either a large number of families or several generations within a large family.
To study the inheritance patterns of genes in humans and other species for which controlled matings are not possible, geneticists use the analysis of pedigrees and populations.
A Pedigree is a pictorial representation of a family history or a family tree, which outlines the inheritance of one or more characteristics.
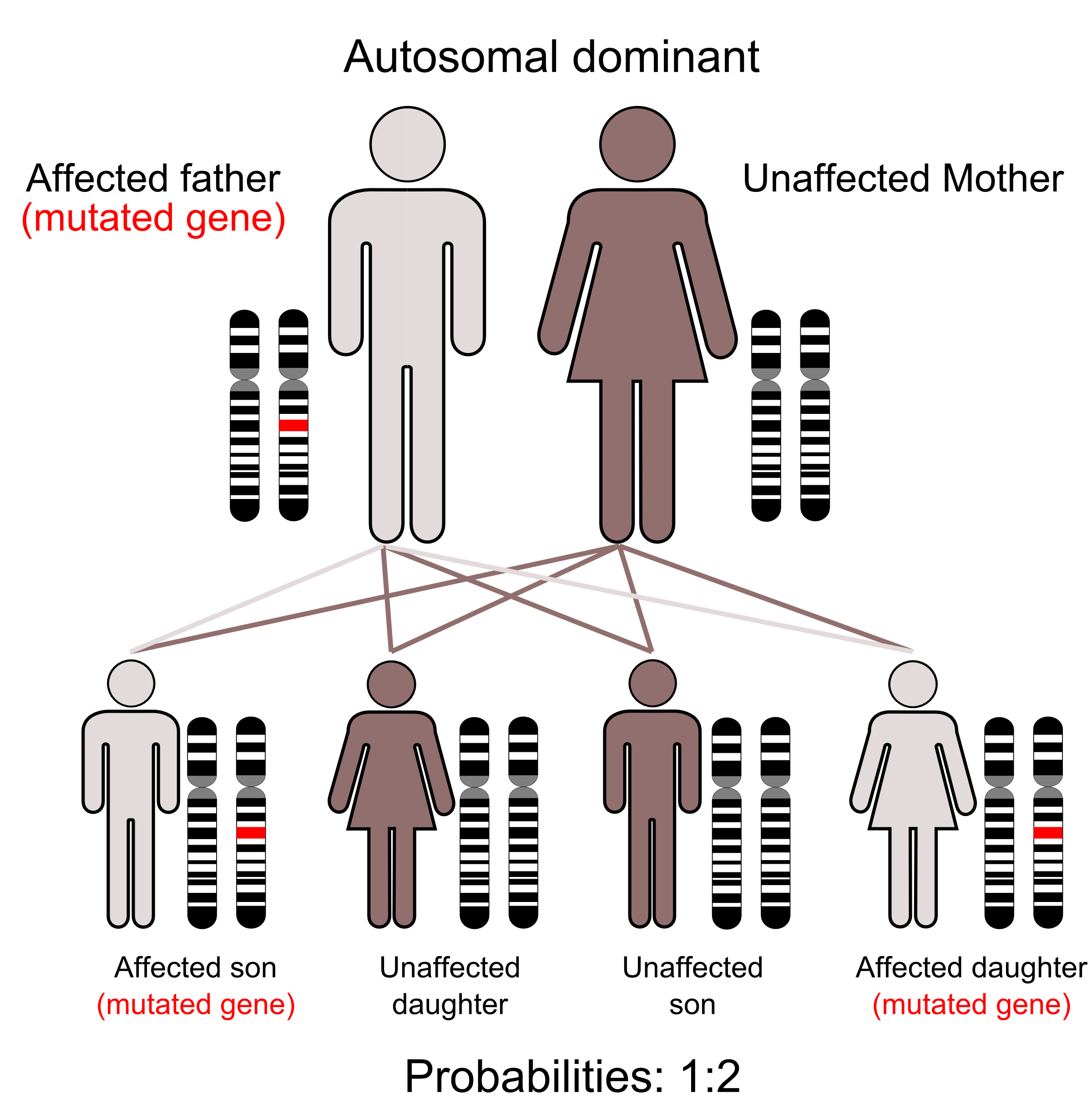
Many traits which run in human families do not exhibit a simple pattern of Mendelian inheritance. This is usually because these traits are coded for by more than one gene. Conversely, traits that are governed by one gene are typically an abnormality that is life-threatening or debilitating — e.g., Huntington’s Disease (caused by a dominant allele) and Cystic Fibrosis (caused by a recessive allele). From a methodical analysis of pedigree charts, we can determine if a particular trait is encoded for by different alleles of a particular (single) gene, as well as if the single-trait gene is recessive or dominant. We may also be able to determine if a trait is autosomal or sex-linked.
Media Attributions
- Figure 4.1.1 Autodominant en 01 by Armin Kübelbeck, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
References
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Cystic Fibrosis. MayoClinic.org (accessed January 18, 2022). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Huntington’s disease. MayoClinic.org (accessed January 18, 2022). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/huntingtons-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356117
Long Description
- Figure 4.1.1 Inheritance of an autosomal dominant trait. Two parents are shown: male possesses the mutated gene, and female is unaffected. Their offspring are outlined, whereby they produce one affected son with the mutated gene, one unaffected son, an unaffected daughter, and finally, an affected daughter with the mutated gene. Alongside each individual is an image of the pair of homologous chromosomes which contains the gene loci for the trait under consideration. Affected individuals are shown via a red shading of the mutated gene locus on an otherwise black and white image of the homologous chromosomes. [Back to Figure 4.1.1]

