9.3 Recombination and Recombination Frequency
The process of meiosis leading to a separation of chromosomes, as well as crossing over, is necessary for the understanding of the process of recombination.
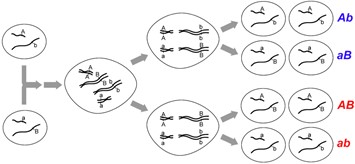
The term “recombination” is used in several different contexts in genetics. In reference to heredity, recombination is defined as a process that results in gametes with combinations of alleles that were not present in the gametes from the parental generation (Figure 9.3.1). Recombination is important because it contributes to the genetic variation that may be observed between individuals within a population and that may be acted upon by selection for evolution.
Watch video, Genetic recombination 1 | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy Medicine, created by Efrat Bruck (2015) at Khan Academy on YouTube (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlnUNmfGn7I).
Inter- and Intrachromosomal Recombination
Interchromosomal recombination occurs either through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different chromosomes. Intrachromosomal recombination occurs through crossovers between loci on the same chromosomes. It is important to remember that in both of these cases, recombination is a process that occurs during meiosis (mitotic recombination may also occur in some species, but it is relatively rare).
As an example of interchromosomal recombination, consider loci on two different chromosomes as shown in Figure 9.3.1 We know that if these loci are on different chromosomes there is no physical connection between them, so they are unlinked and will segregate independently as did Mendel’s traits. The segregation depends on the relative orientation of each pair of chromosomes at metaphase. Since the orientation is random and independent of other chromosomes, each of the arrangements (and their meiotic products) is equally possible for two unlinked loci as shown in Figure 9.3.1.
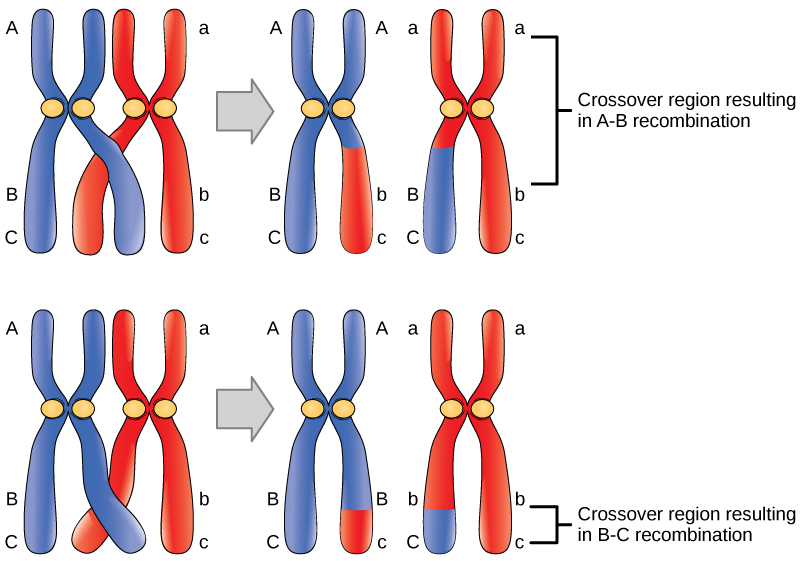
Intrachromosomal recombination occurs through crossovers. Crossovers occur during prophase I of meiosis, when pairs of homologous chromosomes have aligned with each other in a process called synapsis. Crossing over begins with the breakage of DNA of a pair of non-sister chromatids. The breaks occur at corresponding positions on two non-sister chromatids, and then the ends of non-sister chromatids are connected to each other resulting in a reciprocal exchange of double-stranded DNA. Generally, every pair of chromosomes has at least one crossover during meiosis, but often multiple crossovers occur in each chromatid during prophase I.
Because interchromosomal recombination occurs through independent assortment, genes in this situation are always unlinked. Intrachromosomal recombination has instances of linked genes, and so they will be the focus of this chapter.
Inheriting Parental and Recombinant Gametes
If we consider only two loci and the products of meiosis result in recombination, then the meiotic products (gametes) are said to have a recombinant genotype. On the other hand, if no recombination occurs between the two loci during meiosis, the products retain their original combinations and are said to have a non-recombinant, or parental genotype. The ability to properly identify parental and recombinant gametes is essential to apply recombination to experimental examples.
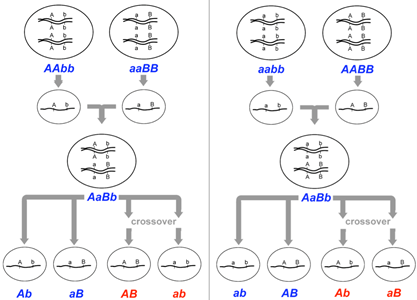
To properly identify recombinant and parental gametes from an individual, you need to know the genotype of its parents (the P generation). This is most easily demonstrated in a dihybrid. If, for two genes, one parent has the genotype A/A B/B, they can only produce one type of gamete: AB. Similarly, if they are a/a b/b, they can also only produce one type of gamete: ab (Figure 9.3.2 right). However, if those two gametes (AB and ab) combine, they create an individual (F1) with a genotype written as A/a B/b. It can be easier to keep track of the parental combinations of gametes by keeping them together when writing the genotype, for this example AB/ab (Figure 9.3.2).
So, the above dihybrid individual can produce four different gametes: AB, ab, Ab and aB. The parental gametes are those that the individual obtained from their parents, in this case AB and ab. Ab and aB are recombinant gametes and are evidence of a recombination event happening, resulting in a different combination of alleles (Figure 9.3.2 right).
For the above example, the P generation has one parent homozygous for both dominant alleles, and the other homozygous for both recessive alleles. It is important to note that this will not always be the case. In some instances, one parent will be homozygous, with one gene dominant and the other gene recessive (A/A b/b), and the other parent will be the opposite (a/a B/B). This situation will change, which is the parental and recombinant gametes (compare left and right in Figure 9.3.2).
Note: Watch the video, Linked Genes, Crossing Over and Genetic Recombination, by AK Lectures (2015) on YouTube.
Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency (RF) is a calculation to define the number of parental and recombinant gametes. The equation is as follows:
[latex]\text{Recombination frequency} = (\frac{\text{No. recombinant progeny}}{\text{Total no. of progeny}})\times{100}\text{%}[/latex]
Through identifying and defining parental and recombinant gametes, you can calculate the RF, and from there, decide the degree of linkage.
Based upon the equation and independent assortment, you can see that the recombination frequency cannot be higher than 0.50. If alleles are assorting independently, there will be a random distribution of alleles in the progeny — 50% will be recombinant gametes and 50% will be parental gametes, making the RF approximately 0.50. If a gene is linked, you will see a higher percentage of parental gametes, making the RF < 0.50. You will never see recombinant gametes more than parental, and in no situation will recombination frequency be higher than 0.50, except slightly with regards to standard experimental error. If you calculate a recombination frequency higher than 0.50, you should ensure that you have accurately defined parental and recombinant gametes.
The video below, Recombination Frequency and Linked Genes, by John Chapman (2013) on YouTube, demonstrates the calculation of recombination frequency based on how often crossing over occurs.
Media Attributions
- Figure 9.3.1 Original by Deyholos (2017), CC BY-NC 3.0, Open Genetics Lectures
- Figure 9.3.2 Original by Deyholos (2017), CC BY-NC 3.0, Open Genetics Lectures
- Figure 9.3.3 Figure 17 02 01 by Rye et al. (2016), CNX OpenStax, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
References
AK Lectures. (2015, January 15). Linked genes, crossing over and genetic recombination (video file). YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=99A6v-5_sFg
Bruck, E./khanacademymedicine. (2015, January 28). Genetic recombination 1 | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy (video file). YouTube. https://youtu.be/BlnUNmfGn7I
Chapman, J. (2013, December 18). Recombination frequency and linked genes (video file). YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nJZCYd4fspY
Deyholos, M. (2017). Figures: 3. When two loci are on non-homologous chromosomes, …; and 4. The genotype of gametes …[digital image]. In Locke, J., Harrington, M., Canham, L. and Min Ku Kang (Eds.), Open Genetics Lectures, Fall 2017 (Chapter 18, p. 4). Dataverse/ BCcampus. http://solr.bccampus.ca:8001/bcc/file/7a7b00f9-fb56-4c49-81a9-cfa3ad80e6d8/1/OpenGeneticsLectures_Fall2017.pdf
Rye, C. et al. (2016, October 21). Figure 17.11 Crossover may occur at different locations on the chromosome [digital image]. In Biology (Chapter 17). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/biology/pages/17-2-mapping-genomes
Long Descriptions
- Figure 9.3.1 Cell division (meiosis) shows non-linked genes and the outcome in gametes. When two loci are on non-homologous chromosomes, their alleles will segregate in combinations identical to those present in the parental gametes (Ab, aB), and in recombinant genotypes (AB, ab) that are different from the parental gametes. [Back to Figure 9.3.1]
- Figure 9.3.2 The genotype of gametes can be inferred unambiguously if the gametes are produced by homozygotes. However, recombination frequencies can only be measured among the progeny of heterozygotes (i.e., dihybrids). The two sets of dihybrids shown here contain different configurations of alleles due to differences in the genotypes of their respective parents. Therefore, different gametes are defined as recombinant and parental among the progeny of the two dihybrids. In one cross, the recombinant gametes will be genotype AB and ab, and in the other cross, the recombinant gametes will be Ab and aB. [Back to Figure 9.3.2]
- Figure 9.3.3 Two sets of homologous chromosomes are paired up during meiosis, showing crossing over of non-sister chromatids in both instances. Depending on the combination and order of alleles on the parental chromosomes, this will determine the nature and variety of recombinant genotypes after crossing over. [Back to Figure 9.3.3]

